Extracellular vesicles in vascular calcification
 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29465447 Vascular calcification is a risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Mechanisms of biomineralization include calcification-competent extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from smooth muscle cells, and macrophages. As opposed to large calcifications, microcalcification accumulation within the plaque fibrous cap can destabilized the plaque causing its rupture. The regulation of EV release and the mechanism in which EVs lead to the formation of microcalcifications remains incompletely understood. We are exploring the role of EVs in cardiovascular physiology and pathology to develop preventive strategies and therapeutic interventions for calcification.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29465447 Vascular calcification is a risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Mechanisms of biomineralization include calcification-competent extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from smooth muscle cells, and macrophages. As opposed to large calcifications, microcalcification accumulation within the plaque fibrous cap can destabilized the plaque causing its rupture. The regulation of EV release and the mechanism in which EVs lead to the formation of microcalcifications remains incompletely understood. We are exploring the role of EVs in cardiovascular physiology and pathology to develop preventive strategies and therapeutic interventions for calcification.
Looking more closely at the aortic valve
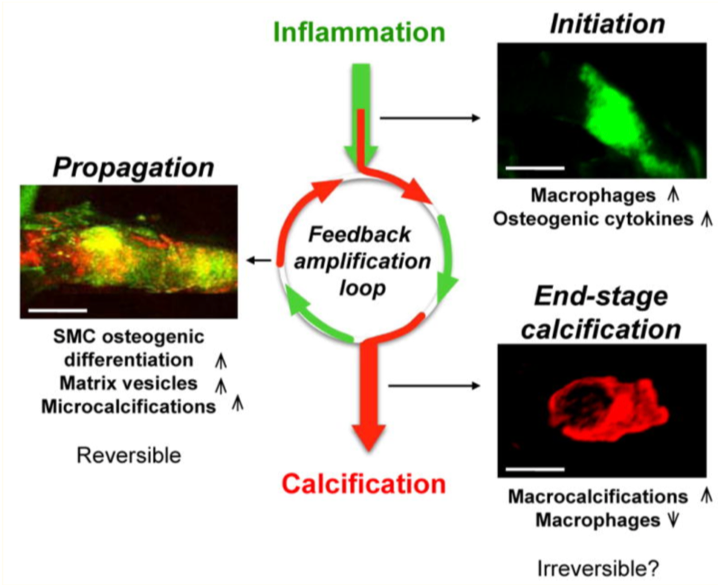 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3139950/ Calcific Aortic valve disease (CAVD) is a dynamic disease that initiates by alterations in valvular cell biology and progresses to leaflet thickening, neovascularization and calcium deposition. The understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of CAVD has been hindered by our inability to identify the dynamic molecular events associated with early calcific changes in valves. We are exploring the mechanisms of aortic valve calcification, which can lead us to target early stages of CAVD, when it can be halted.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3139950/ Calcific Aortic valve disease (CAVD) is a dynamic disease that initiates by alterations in valvular cell biology and progresses to leaflet thickening, neovascularization and calcium deposition. The understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of CAVD has been hindered by our inability to identify the dynamic molecular events associated with early calcific changes in valves. We are exploring the mechanisms of aortic valve calcification, which can lead us to target early stages of CAVD, when it can be halted.
Macrophage Notch Ligand Delta-like 4 in Cardiometabolic Diseases
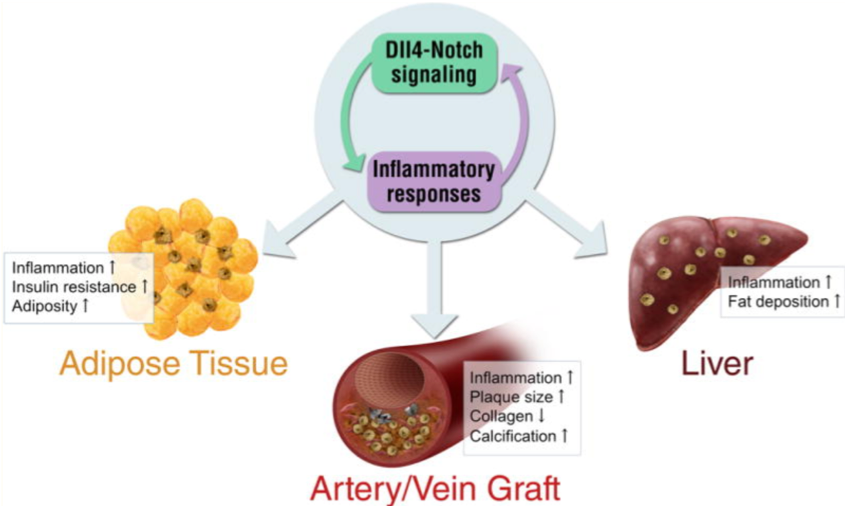 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5033717/ Macrophage activation plays a key role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic vascular disease and metabolic disorders. Dll4-mediated Notch signaling regulates the balance of macrophage phenotypes. We are exploring the role of Dll4-Notch axis in macrophage activation. Our studies will lead us to develop innovative therapies for cardiovascular diseases, that may restore a normal microenvironment by controlling excessive pro-inflammatory programs without compromising anti-inflammatory or pro-resolving mechanisms.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5033717/ Macrophage activation plays a key role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic vascular disease and metabolic disorders. Dll4-mediated Notch signaling regulates the balance of macrophage phenotypes. We are exploring the role of Dll4-Notch axis in macrophage activation. Our studies will lead us to develop innovative therapies for cardiovascular diseases, that may restore a normal microenvironment by controlling excessive pro-inflammatory programs without compromising anti-inflammatory or pro-resolving mechanisms.